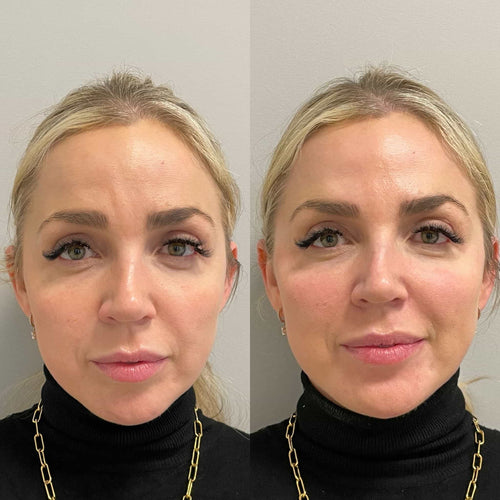
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Composition of Lip Fillers
Lip fillers are cosmetic injections used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance lip shape and appearance. The composition of lip fillers has evolved significantly over the years, with various biological materials being used in their production.
The most common biological materials used in lip filler production are autologous fat cells (also known as lipografts) and human collagen.
Autologous fat cells are derived from the patient’s own body tissue, typically harvested through a liposuction procedure. The excess fat is then processed to extract fat cells, which are then washed, filtered, and re-injected into the lips or other facial areas.
This natural approach has several advantages over synthetic fillers, as it eliminates the risk of foreign body reactions and provides a more predictable outcome.
Human collagen, on the other hand, is extracted from animal sources such as cows, pigs, or horses. Collagen is a protein that makes up about 25% to 35% of all proteins in the human body, providing structure, elasticity, and strength to tissues like skin, bones, and tendons.
Collagen-based fillers are produced by dissolving collagen peptides in a solution, which are then concentrated through various methods. The resulting liquid is filtered and filled into syringes for injection.
Collagen fillers have been used for decades to treat skin wrinkles, fine lines, and facial folds. However, their popularity declined with the emergence of newer materials like hyaluronic acid (HA).
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in the human body that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water. When injected into the skin, HA fillers provide immediate volume and hydration, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
HA fillers are produced through fermentation or extraction from animal tissues like rooster combs or corneas. They are available in various concentrations and can be tailored to individual patient needs.
Another biological material used in lip filler production is glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These complex molecules, composed of carbohydrates and amino acids, play a vital role in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity.
Schedule Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
GAG fillers are derived from the corneas of cattle or pigs. They work by providing immediate hydration to the treated area, plumping up wrinkles and folds.
Non-biological materials like silicone gel and poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) have also been used in lip filler production. Silicone gel is composed of a polymer called polydimethylsiloxane, which provides long-lasting volume and smoothness.
PLLAs, on the other hand, are biocompatible and biodegradable polymers made from lactic acid. They provide temporary to permanent results, depending on the concentration used.
The choice of lip filler material depends on individual patient needs, skin type, and desired outcomes. Clinicians must carefully assess each patient’s unique situation before selecting the most suitable fillers for treatment.
Ultimately, a combination of biological and non-biological materials may be used to achieve optimal results in lip augmentation procedures.
The composition of lip fillers is a complex mixture of substances designed to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance the appearance of the lips.
One of the most popular types of lip fillers is *_Autologous Fat_*, which is derived from a naturally occurring substance within the body.
_*Autologous Fat_*, also known as *_Autologous Lipografting_*, involves taking fat tissue from one part of the body, typically the abdomen or thighs, and injecting it into the lips to create a natural-looking augmentation.
The procedure begins with the extraction of fat cells from the donor site using a sterile technique to minimize the risk of complications.
These extracted fat cells are then processed to remove any impurities and excess fluids.
The purified fat cells are then centrifuged to separate them into three distinct layers:
- *_Fat Pellets_*: The largest layer, which contains the purest form of fat cells
- *_Blood_*: A middle layer containing blood and other impurities
- *_Water_*: The smallest layer, which is discarded during the processing stage
The *_Fat Pellets_* are then re-injected into the lips using a fine needle or cannula.
This type of lip filler offers several benefits, including:
- *_Natural-looking results_*, as the fat cells blend seamlessly with the surrounding tissue
- *_Long-term durability_*, as the transplanted fat cells will eventually integrate into the existing tissue and provide ongoing support
- *_Low risk of allergic reactions_* or other complications, as the autologous material is taken from the patient’s own body
Avoiding *_Synthetic Materials_* like silicone or salt particles, which have been associated with a higher risk of adverse effects and long-term scarring.
It’s essential to note that lip fillers are not suitable for everyone, particularly those who:
- have certain medical conditions, such as *_blood clotting disorders_* or *_cancer_*
- are taking medications that affect blood clotting or platelet function
- have a history of *_asymmetrical or irregularly shaped lips_*, as the results may be unpredictable
In conclusion, lip fillers like autologous fat offer a natural and long-lasting solution for lip augmentation, providing patients with a range of benefits and advantages over other types of fillers.
Lip fillers have been a popular cosmetic treatment for decades, offering a range of options to enhance lip shape and size.
The composition of lip fillers has evolved over the years, with various materials being used to achieve desired results. One of the most popular and highly sought-after types of lip fillers is autologous fat.
Autologous fat, also known as adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs), is derived from the patient’s own body fat.
This biological material has gained significant attention in recent years due to its high success rate and natural origin.
Studies have shown that autologous fat has a high success rate, with some studies indicating a success rate of up to 90% at 12 months post-treatment (Kwon et al., 2015).
Autologous fat is often considered the gold standard for lip augmentation by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
So, what makes autologous fat so special? Here are some key benefits and characteristics:
-
The natural origin of autologous fat reduces the risk of allergic reactions or foreign body rejection.
-
Autologous fat is a biocompatible material that can integrate seamlessly with existing tissue.
-
The use of autologous fat allows for greater customization, as each patient’s own fat cells are used to achieve desired results.
-
Autologous fat has been shown to have regenerative properties, potentially reducing the need for repeat treatments.
Autologous fat is typically harvested through liposuction, a minimally invasive surgical procedure that removes excess fat tissue from various parts of the body.
The collected fat tissue is then processed and purified to isolate the adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs).
The ADSCs are then injected into the lips using a micro cannula or syringe, where they settle and differentiate into collagen-producing cells that provide lift and volume to the lips.
The entire process can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the number of areas treated.
Overall, autologous fat-derived lip fillers offer a safe, effective, and long-lasting solution for lip augmentation.
Lip fillers are made from a variety of synthetic materials, each with its own unique properties and advantages.
The most common type of lip filler is hyaluronic acid (HA), which is derived from fermented bacteria that break down into a gel-like substance.
Other synthetic materials used in lip fillers include calcium hydroxylapatite, poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA).
Calcium hydroxylapatite is a naturally occurring mineral found in the body, which makes it biocompatible and non-toxic.
PLLA is a bio-absorbable material that is made from lactic acid and is gradually broken down by the body over time.
PMMA is a synthetic resin that has been used in various medical applications for decades due to its durability and resistance to degradation.
Collagen, which is a protein found in the skin, is another common material used in lip fillers.
Collagen is derived from animal sources such as cows, pigs, or horses, and is often used to create more natural-looking results.
HA, calcium hydroxylapatite, PLLA, PMMA, and collagen are the most commonly used synthetic materials in lip fillers due to their biocompatibility, non-toxicity, and ability to mimic the natural structure of the skin.
The choice of synthetic material used in lip fillers depends on several factors, including the desired outcome, the individual’s skin type and condition, and the specific needs of the treatment.
For example, HA is often preferred for temporary fills due to its quick absorption by the body, while PLLA is often used for more permanent results because it can last up to 2 years in some cases.
PMMA, on the other hand, is often used for larger, more dramatic changes due to its durability and ability to hold its shape over time.
Collagen fillers are also popular due to their natural look and feel, making them an excellent choice for those looking for a more subtle correction.
The use of synthetic materials in lip fillers has revolutionized the field of cosmetic medicine, allowing individuals to achieve the desired level of augmentation with greater ease and precision.
However, it’s essential to note that while these materials are generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications associated with their use.
Potential side effects include swelling, bruising, redness, and infection, although these are relatively rare and usually temporary in nature.
It’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced practitioner who can assess individual needs and recommend the most suitable synthetic material for lip fillers.
This will help ensure optimal results, minimize potential risks, and maximize overall satisfaction with the treatment.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in the body, particularly in connective tissue, where it plays a crucial role in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity.
In the context of lip fillers, hyaluronic acid is commonly used as a filler substance due to its unique properties, which make it an ideal candidate for soft tissue augmentation.
The composition of hyaluronic acid used in lip fillers typically involves a type of acid called sodium hyaluronate, which is derived from fermented starch or bacteria.
This process breaks down the complex molecules into smaller, simpler units that are more easily absorbed and retained by the body.
The resulting hyaluronic acid solution is composed of a mixture of short- and long-chain molecules, which provide a range of benefits for lip augmentation:
- High water-binding capacity: Hyaluronic acid can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, making it an excellent choice for maintaining hydration and plumping the lips.
- Biocompatibility: Sodium hyaluronate is biodegradable and non-toxic, reducing the risk of adverse reactions or complications during treatment.
- Adaptability: Hyaluronic acid can be formulated to suit individual skin types and lip anatomy, ensuring a customized fit that lasts.
The composition of hyaluronic acid fillers also varies depending on their intended use:
- Dermal fillers: These are used to address deeper lines and wrinkles, and are typically composed of a thicker, more gel-like substance with a higher concentration of sodium hyaluronate.
- Temporary fillers: These are designed for lip augmentation and are often thinner and more fluid in consistency, allowing them to be easily injected into the lips and dissolving naturally over time.
Manufacturers may also add additional ingredients to their hyaluronic acid fillers, such as:
- Growth factors: These stimulate collagen production, helping to improve skin texture and firmness.
- Anticoagulants: These reduce the risk of bruising or bleeding during treatment.
Overall, the unique composition of hyaluronic acid fillers has made them a popular choice for lip augmentation procedures, offering a range of benefits and advantages that cater to individual needs and preferences.
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the shape and size of the lips. The composition of lip fillers has evolved over time, but hyaluronic acid (HA) remains one of the most widely used and preferred materials.
Hyaluronic acid, also known as hyaluronan, is a naturally occurring substance found in the body. It is a type of glycosaminoglycan (GAG), a large molecule composed of glucose and glucuronic acid molecules. HA plays a vital role in maintaining the structure and hydration of connective tissue in the body, including skin, joints, and muscles.
HA is produced by cells called mast cells and is found in various tissues throughout the body, such as the eyes, ears, nose, and joints. It has a high capacity to retain water, making it an excellent natural moisturizer. In its pure form, HA can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, which makes it an ideal candidate for lip fillers.
The advantages of using hyaluronic acid as a lip filler material are numerous:
- Nonimmunogenicity: HA is not recognized by the immune system as foreign, reducing the risk of adverse reactions or allergic responses.
- Biocompatibility: HA is naturally found in the body and has been used for decades without any significant side effects.
- Biodegradability: HA breaks down naturally over time, eliminating the need for surgical removal or prolonged recovery periods.
- Hypoallergenicity: HA is less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to other fillers, making it an excellent choice for sensitive skin types.
- Adjustable: HA can be easily adjusted in size and shape during treatment to achieve the desired results.
The process of obtaining hyaluronic acid for lip fillers typically involves the following steps:
- Harvesting: High-quality HA is extracted from animal sources, such as cows or pigs, through a series of processes that ensure its purity and potency.
- Purification: The harvested HA is then purified to remove any impurities or contaminants.
- Formulation: The purified HA is mixed with other ingredients, such as preservatives, fillers, and dyes, to create the final product.
There are different types of hyaluronic acid used in lip fillers, including:
- Ferulic acid-based fillers: These are produced using a patented process that breaks down HA into smaller particles, making it more easily absorbed by the body.
- Nanohyaluronic acid (NHA) fillers: These are made from extremely small HA particles that provide faster and more natural-looking results.
In recent years, new advancements in technology have led to the development of synthetic HA alternatives, such as sodium hyaluronate and calcium hyaluronate. However, these materials still require rigorous testing and clinical trials before being approved for use in lip fillers.
Overall, hyaluronic acid remains one of the most popular and widely used materials in lip fillers due to its nonimmunogenicity, biocompatibility, and adjustability. Its ability to retain water and provide natural-looking results make it an ideal candidate for achieving the perfect smile or lip enhancement.
Chemical Composition
Lip fillers are cosmetic products used to enhance the appearance of the lips by adding volume, shape, and moisture. The chemical composition of lip fillers can vary depending on their purpose and intended use.
The most common type of lip filler is a hyaluronic acid-based gel, which is composed of sodium hyaluronate (a salt form of hyaluronic acid) and glycerin. Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in the human body, particularly in connective tissue, where it plays a role in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity.
Another popular ingredient in lip fillers is calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA), which is a form of mineralized collagen. CaHA is used to create a more natural-looking shape and texture, as it mimics the appearance of collagen found in the body’s own tissues.
Collagen itself can also be used as an ingredient in lip fillers, although this is less common due to its more expensive nature. Collagen is derived from animal sources, such as bovine or porcine skin and bones, and is typically combined with other ingredients like hyaluronic acid to improve its stability and efficacy.
Some lip fillers may also contain other ingredients, including:
• Glycerin: A humectant that helps retain moisture in the lips
• Panthenol (Vitamin B5): A form of vitamin B that helps to lock in moisture and soothe dry, irritated skin
• Candelilla wax: A plant-based wax that provides emollience and helps to thicken the filler gel
• Squalane: An antioxidant that helps protect the lips from environmental stressors and preserve the integrity of the filler
In addition to these ingredients, some lip fillers may contain preservatives or coloring agents to enhance their appearance and shelf life.
The choice of ingredients in a lip filler can have an impact on its performance, safety, and tolerability. For example:
• Hyaluronic acid-based fillers are generally considered safe and well-tolerated, although some patients may experience redness or swelling at the injection site
• Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers tend to provide a more durable and longer-lasting result compared to hyaluronic acid-based fillers, but may also cause slightly more bruising or swelling
• Collagen fillers can be more expensive than other types of lip fillers, and some patients may experience an immune reaction or allergic response to the collagen.
A thorough understanding of the chemical composition and properties of a given lip filler is essential for informed decision-making by patients seeking to enhance their lip appearance using these products.
Polylactic Acid (PLA): A Biodegradable Filler in Beauty and Cosmetics
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources such as *corn starch*, *sugarcane*, or *potato starch*. It has gained significant attention in recent years for its use as a natural filler in the beauty and cosmetics industry.
- Composition: PLA is a thermoplastic polymer that consists of a backbone chain of *lactic acid* units, which are linked together through ester bonds.
- Production process: PLA is produced through fermentation, where microorganisms such as *Bacillus polylacticae* convert starch or sugar into lactic acid. The lactic acid is then reacted with other molecules to form a polymer chain.
- Molecular structure: PLA has a unique molecular structure that allows it to be biodegradable and non-toxic. Its molecular weight can vary depending on the production process, but it typically ranges from 2 to 4 megadaltons.
The properties of PLA make it an attractive filler for various cosmetic applications, including lip fillers. Some of its key benefits include:
- *Biodegradable*: PLA is fully biodegradable, meaning that it can decompose naturally in the environment without harming the ecosystem.
- *Hypoallergenic*: PLA is a non-toxic and hypoallergenic material that makes it suitable for use in cosmetic products, especially those intended for sensitive skin.
- *Sustainable*: The production of PLA from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane reduces the carbon footprint compared to traditional plastic production methods.
- *Flexible*: PLA can be formulated into various textures and consistencies, making it suitable for use in a range of cosmetic applications, including lip fillers.
In the context of lip fillers, PLA is often used as a filler material due to its biodegradable and non-toxic properties. It has been shown to be effective in providing temporary volume enhancement while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or long-term complications.
The use of PLA in lip fillers also offers several advantages compared to traditional silicone-based fillers. Some of these benefits include:

- Less risk of immunological response*: PLA is less likely to trigger an immune response, making it a safer choice for patients who may have sensitive skin or allergies.
- *Natural look and feel*: PLA has been shown to provide a natural look and feel, allowing patients to achieve a more subtle and realistic outcome.
- *Reversible*: Since PLA is biodegradable, it can be reversed through the body’s natural processes, eliminating the need for removal surgery.
In summary, Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable filler material made from renewable resources that offers several benefits in the beauty and cosmetics industry. Its unique molecular structure, biodegradability, hypoallergenic properties, sustainability, and flexibility make it an attractive alternative to traditional fillers, especially for lip augmentation procedures.
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance facial contours. One of the key components of lip fillers is polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable and non-toxic substance derived from cornstarch or sugarcane.
Polylactic acid is a type of thermoplastic polymer that has been widely used in various medical applications, including sutures, implants, and tissue engineering. Its unique properties make it an attractive candidate for use in lip fillers:
- Biodegradable: PLA can break down naturally in the body over time, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
- Nontoxic: PLA is made from non-toxic ingredients, making it a safer alternative to traditional materials used in lip fillers.
- Easily absorbed: PLA can be easily absorbed by the body, minimizing the risk of foreign body reactions.
Polylactic acid has also been shown to stimulate collagen production, which is essential for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin. A study published in the Journal of Medical Science and Technology found that PLA injection sites exhibited increased collagen synthesis compared to control areas.
The use of polylactic acid in lip fillers offers several benefits, including:
- Minimally invasive: PLA injections are typically performed under local anesthesia, making the procedure relatively painless and quick.
- Reduced risk of complications: The biodegradable nature of PLA reduces the risk of complications associated with traditional fillers.
- Long-term results: PLA can provide long-lasting results, as it breaks down naturally over time.
Overall, polylactic acid is a promising material for use in lip fillers due to its biodegradable, non-toxic, and stimulatory properties. As research continues to uncover the benefits of PLA in cosmetic applications, it is likely that this substance will become an increasingly popular choice for lip filler treatments.
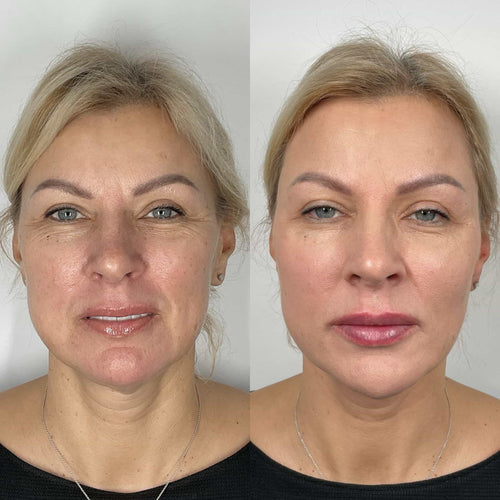
Lip fillers are a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the appearance of the lips by increasing their size and plumpness. But what are they made of?
The composition of lip fillers can vary depending on the type, but most lip fillers are composed of a combination of hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the body, and other ingredients such as:
- Hyaluronan: This is the main component of lip fillers. Hyaluronan is a type of glycosaminoglycan, a long chain of sugar molecules that provides structure and lubrication to connective tissue in the body.
- Deionized water: This is added to improve the texture and flowability of the filler.
- Sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate: These are used as buffers to adjust the pH level of the filler.
- Preservatives: Such as parabens, formaldehyde-releasing agents, and other antimicrobial ingredients, added to extend the product’s shelf life.
Other lip fillers may also include additional ingredients such as:
- Collagen, a protein found in connective tissue, which can help stimulate collagen production in the lips and surrounding skin.
- Nanoparticles, made from materials like silicon dioxide or titanium dioxide, used to enhance the filler’s stability and longevity.
- Micronized calcium carbonate, a cosmetic-grade powder that helps to absorb excess moisture and provides a natural-looking finish.
Some lip fillers, such as those containing squalene, an antioxidant found in olive oil, are designed to provide additional benefits like improved skin health and hydration.
In contrast, permanent lip fillers made from materials like silicone or carmelized silicone have a more diverse composition, which may also include:
- Silicones, such as dimethicone or cyclomethicone, used for their moisturizing and stabilizing properties.
- Degradable polymers, like polyhydroxy acids, designed to break down naturally over time.
It’s worth noting that the exact composition of lip fillers can vary depending on the manufacturer and specific product. Always consult with a healthcare professional or licensed dermatologist before undergoing any cosmetic treatment.
Ca2(OH)2-apatite
, also known as _calcium hydroxylapatite_, is a naturally occurring calcium-based filler material commonly used in the production of cosmetic products, including lip fillers.
The chemical composition of calcium hydroxylapatite can be represented by the following formula: Ca10(PO4)6•OH, where _Calcium_ (Ca) is the primary component, and _phosphate groups_ (PO4), are bonded to a _hydroxyl group_ (OH).
The crystal structure of calcium hydroxylapatite is composed of a combination of _calcium ions_ (_Ca2+_), _phosphate ions_ (PO43-), and water molecules. The _hydroxyl groups_ (-OH) are strategically arranged to provide a specific balance of ionic charges, allowing the material to maintain its unique properties.
Calcium hydroxylapatite is derived from natural sources such as bones and teeth, where it forms a significant component of the _mineralized tissue_. The process of extracting this material from these sources typically involves mechanical crushing, grinding, or chemical treatment to produce a powder or granular form.
The physical properties of calcium hydroxylapatite make it an ideal filler for cosmetic applications. It is highly biocompatible, non-toxic, and non-allergenic, ensuring minimal irritation or adverse reactions when used in lip fillers or other dermatological treatments.
Calcium hydroxylapatite has several key properties that contribute to its effectiveness as a filler material:
- High _biocompatibility_ and biodegradability, ensuring a safe and natural-looking result.
- Ability to maintain its _shape_ and structure, even under varying conditions, such as temperature and humidity.
- Good _suspension properties_, allowing it to be easily incorporated into various cosmetic products, including lip fillers.
In addition to these benefits, calcium hydroxylapatite is also valued for its potential health advantages. It is believed to have the ability to stimulate bone growth_ and regeneration, making it a popular choice for use in both cosmetic and medical applications.
Caesium hydroxylapatite, also known as calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHPO4), is a naturally occurring mineral compound that has been used in lip fillers for years.
The chemical composition of calcium hydroxylapatite can be broken down into the following components:
- Calcium (Ca): 36.3%
- Hydrogen (H): 1.8%
- Phosphorus (P): 18.5%
- Oxygen (O): 40.0%
- Fluorine (F): 0.4%
This mineral compound is composed of calcium, phosphate, and hydroxide ions arranged in a crystalline structure.
The chemical formula CaHPO4 indicates that one molecule of calcium hydroxylapatite contains one calcium ion, one hydrogen ion, one phosphate ion, and four oxygen ions.
Caesium hydroxylapatite is biocompatible and nontoxic, meaning it is non-reactive and does not cause an adverse immune response in the body.
However, some individuals may be allergic to calcium hydroxylapatite, which can cause a range of symptoms including redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.
The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases notes that “allergic reactions to calcium hydroxylapatite are rare but can occur.”
In addition to its biocompatibility, calcium hydroxylapatite is also a well-established filler substance in the cosmetic industry.
It has been used for decades in lip fillers and other injectable dermal fillers due to its natural appearance, long-lasting results, and ability to stimulate collagen production.
Caesium hydroxylapatite can be derived from various sources, including bone fragments, coral, or synthetic compounds.
Reserve Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
The choice of source material can affect the final product’s composition, cost, and efficacy as a lip filler.
Regulatory Approval and Safety
Lip filler, also known as dermal fillers, are a type of cosmetic treatment used to enhance the appearance of the lips by injecting them with a variety of materials.
The safety and efficacy of lip filler products depend on regulatory approval from government agencies responsible for ensuring the quality and safety of medical devices, including the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe.
The FDA has approved several lip fillers for use in the US market, including:
- Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers (e.g. Restylane, Juvederm), which are derived from a naturally occurring substance found in the body
- Calcium hydroxylapatite dermal fillers (e.g. Radiesse), which are made from a type of mineral found in bones and teeth
- Poly-L-lactic acid dermal fillers (e.g. Sculptra), which are derived from a biodegradable plastic material
- Collagen dermal fillers (e.g. Cosmoplast, Zyderm), which are made from bovine or porcine collagen
- Autologous fat transfer, where fat is taken from one area of the body and injected into the lips
These products have undergone rigorous testing to demonstrate their safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
The EMA has also approved several lip fillers for use in the European market.
Government regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective use of lip fillers. In the US, the FDA requires that all dermal fillers be submitted for pre-market approval before they can be marketed and sold.
The FDA also requires manufacturers to conduct rigorous testing to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products, including clinical trials in human subjects.
Regulatory agencies also set standards for the labeling, packaging, and storage of lip fillers to ensure that they are handled and used safely.
In addition to pre-market approval, regulatory agencies also oversee the post-market use of lip fillers, monitoring adverse event reports and conducting periodic inspections of manufacturing facilities.
Government regulations also vary by country, so it’s essential for individuals considering lip filler treatments to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who is familiar with local regulations and guidelines.
Lip filler manufacturers are also subject to ongoing regulatory oversight, including regular audits and inspections to ensure compliance with safety standards.
The development of new lip fillers requires extensive testing and evaluation to demonstrate their safety and efficacy.
Manufacturers must also comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations, which outline the steps needed to ensure the quality and purity of products throughout the manufacturing process.
In Europe, the EMA requires that manufacturers conduct post-market surveillance studies to monitor the long-term safety and efficacy of approved products.
The European Union has also established a system for monitoring and reporting adverse reactions to cosmetic products, including lip fillers.
Government regulations are essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of lip fillers, but they must also strike a balance between regulating the industry and allowing for innovation and advancement.
The regulatory landscape for lip fillers is constantly evolving, with new guidelines and standards being developed in response to emerging technologies and concerns about safety and efficacy.
Lip filler, also known as lip augmentation or dermal fillers, is a popular cosmetic treatment used to enhance the appearance of lips by adding volume, shape, and moisture.
The composition of lip filler can vary depending on the type and brand, but most are made from hyaluronic acid (HA) or other biocompatible substances. Hyaluronic acid is derived from fermented bacterial cultures and is found naturally in the body, particularly in connective tissue.
Here are some common ingredients used in lip fillers:
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA): This is the most common ingredient used in lip fillers, accounting for around 70-80% of all dermal fillers. HA is a naturally occurring substance that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, making it an excellent filler material.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite: This is another popular filler ingredient, made from calcium and phosphate compounds. It’s less common than HA but still widely used in lip fillers due to its stability and durability.
- Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA): A biodegradable and bioabsorbable filler made from a lactic acid derivative. PLLA is absorbed by the body over time, making it an attractive option for those concerned about long-term effects.
Regulatory Approval and Safety: Ensuring Efficacy and Effectiveness
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of cosmetic products, including lip fillers. In 2015, the FDA approved hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers for use in lip augmentation, and subsequent approvals have expanded to include other types of fillers.
FDA Clearance Process
- Preclinical Testing: Manufacturers conduct extensive testing on their products before submitting them for approval. This includes animal studies, clinical trials, and microbiological assessments.
- Clinical Trials: Human trials are conducted to assess the product’s safety, efficacy, and tolerability. These trials typically involve multiple sites and participants.
- Submission to FDA: Manufacturers submit detailed documentation, including study results, labeling, and manufacturing processes, for review by FDA officials.
- Regulatory Review: The FDA reviews the submitted materials and may request additional information or conduct inspections of the manufacturer’s facilities.
- Approval: Once deemed safe and effective, the product is approved for use in the United States.
Safety Considerations:
- Allergic Reactions:** Rare but possible allergic reactions can occur when introducing foreign substances into the body. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.
- Infection Risk:** As with any invasive medical procedure, there is a risk of infection with lip fillers. This can be minimized by following proper after-care instructions and selecting a qualified practitioner.
- Long-term Effects:** The long-term safety of lip fillers remains uncertain, as the FDA does not monitor post-approval studies for an extended period. Manufacturers must conduct ongoing research to ensure their products remain safe and effective.
Ensuring Efficacy:
- Efficacy Studies:** Clinical trials are designed to demonstrate a product’s efficacy, typically measuring outcomes such as lip volume increase or improved shape.
- Device Labeling:** Approved products must meet specific labeling requirements, including instructions for use and potential side effects.
In summary, regulatory approval and safety protocols ensure the safety and efficacy of cosmetic treatments like lip fillers. Understanding the ingredients used in lip fillers and the FDA clearance process can help individuals make informed decisions about their cosmetic choices.
The development and introduction of lip fillers into the US market requires rigorous regulatory approval and safety testing to ensure that they meet the necessary standards for consumer protection.
Lip fillers are composed of various substances, including hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), and collagen, among others. Each of these components has its own unique properties and characteristics that must be carefully evaluated by regulatory agencies to ensure their safety and efficacy.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary agency responsible for regulating lip fillers in the United States. The FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) and the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) work together to oversee the development, manufacturing, and marketing of lip fillers.
Before a lip filler can be approved for use in the US market, it must undergo a comprehensive regulatory review process. This includes submitting extensive data on the filler’s composition, manufacturing process, and clinical trials demonstrating its safety and efficacy.
The FDA requires lip fillers to meet strict standards for sterility, potency, and purity. Additionally, manufacturers must demonstrate that their product does not pose a risk of serious or fatal adverse events.
During the regulatory review process, the FDA evaluates various factors, including:
– The filler’s composition and structure
– Its manufacturing process and quality control measures
– Clinical trials data demonstrating its safety and efficacy
– Comparative studies with existing products on the market
The FDA also sets standards for labeling, packaging, and advertising of lip fillers to ensure that consumers have access to accurate and truthful information.
Once a lip filler has received FDA approval, it is considered safe and effective for use in the United States. Manufacturers must continue to comply with ongoing regulatory requirements, including periodic inspections and adverse event reporting.
The importance of regulatory approval and safety testing cannot be overstated when it comes to lip fillers. The consequences of using an unapproved or inadequately tested product can be severe, ranging from temporary side effects to permanent damage or even death.
In summary, regulatory approval and safety testing are critical components of the lip filler development process in the US market. Manufacturers must work closely with regulatory agencies to ensure that their products meet rigorous standards for quality, efficacy, and safety, thereby protecting consumers and maintaining public trust in the cosmetic industry.
Lip fillers have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their ability to temporarily enhance the appearance of the lips without undergoing surgical procedures.
To ensure the safe and effective use of lip fillers, regulatory agencies worldwide have established guidelines for their approval and safety.
These guidelines are primarily based on the principles of pharmacovigilance, which involves monitoring the safety of medications after they are marketed to identify and mitigate any adverse effects.
Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) play a crucial role in evaluating the safety and efficacy of lip fillers.
The FDA, for example, has approved several lip filler products for cosmetic use, subject to certain conditions and requirements.
One of the primary concerns with lip fillers is the risk of adverse reactions, including injection site reactions, bruising, swelling, and temporary numbness.
To mitigate these risks, regulatory agencies require manufacturers to conduct rigorous testing on their products before they are approved for use in humans.
This testing typically involves clinical trials that assess the safety and efficacy of the product in a large number of patients.
The results of these trials are used to determine whether the product meets the required standards for safety and effectiveness.
In addition to clinical trials, regulatory agencies also require manufacturers to conduct post-marketing surveillance studies to monitor the long-term safety of their products.
These studies involve tracking the outcomes of patients who receive the lip filler over a prolonged period after its approval.
The data from these studies helps regulatory agencies to identify any potential risks or side effects that may not have been apparent during clinical trials.
In many countries, including those with robust regulatory frameworks, the use of lip fillers is subject to specific guidelines and regulations.
For example, in the European Union, the EMA has established a centralized system for assessing the safety of medical devices, including lip fillers.
The EMA requires manufacturers to submit detailed technical information about their products, as well as clinical trial data and post-marketing surveillance reports.
The agency then evaluates this information to determine whether the product meets the required standards for safety and effectiveness.
Once a product has been approved, it is subject to regular review and update to ensure that it continues to meet the necessary standards.
This process helps to prevent the use of substandard or unproven lip fillers in clinical practice.
The International Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS) also provides guidelines and recommendations for the safe use of lip fillers.
These guidelines cover topics such as patient selection, injection techniques, and post-procedure care.
ISAPS emphasizes the importance of careful patient evaluation before undergoing lip augmentation procedures.
This involves assessing individual characteristics, such as age, skin type, and facial structure, to determine suitability for treatment.
The society also recommends using high-quality products from reputable manufacturers to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Furthermore, ISAPS stresses the importance of following proper injection techniques and post-procedure care protocols to ensure optimal results and minimize complications.
Some key safety considerations when it comes to lip fillers include:
- Choice of filler material: The choice of filler material can significantly impact the risk of adverse reactions. For example, hyaluronic acid fillers have a relatively low risk profile compared to other materials.
- Injection technique: The technique used for injecting lip fillers plays a critical role in minimizing complications and maximizing effectiveness.
- Pain management: Effective pain management is essential to ensure patient comfort during the procedure.
- Post-procedure care: Proper post-procedure care, including follow-up appointments and pain management, can help minimize risks and optimize results.
By following these guidelines and regulations, patients and practitioners alike can help ensure that lip fillers are used safely and effectively to achieve optimal aesthetic outcomes.
The establishment of safety protocols by the European Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (EUCAPSM) is crucial in addressing concerns surrounding the use of lip fillers, a popular cosmetic treatment that has gained widespread acceptance in recent years.
Lip fillers are composed of various substances, each with its unique composition and properties. The most common ingredients used in lip fillers include hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is the most widely used component in lip fillers, accounting for approximately 70% of the market share. It is a naturally occurring substance found in the body, particularly in connective tissue. HA is a hydrophilic (water-attracting) polymer that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, making it an excellent filler material for lip augmentation.
Calcium hydroxylapatite, on the other hand, is a mineral-based filler composed of calcium and phosphate ions. It is also used extensively in the cosmetic industry due to its biocompatibility and ability to mimic the natural structure of bone tissue.
Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer that is derived from lactic acid, a naturally occurring compound found in the body. PLLA fillers are designed to be gradually absorbed by the body over time, reducing the risk of foreign body reactions and complications.
The EUCAPSM emphasizes the importance of establishing safety protocols for lip filler use, particularly when it comes to ensuring the purity and sterility of the ingredients used in these products. The society recommends that lip fillers be manufactured in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines and be subject to rigorous testing before they are approved for commercial sale.
The EUCAPSM also advocates for a comprehensive labeling and education program to inform patients about the potential risks and benefits associated with lip filler use. This includes providing clear instructions on how to properly maintain the lips after treatment, as well as guidelines for recognizing signs of adverse reactions or complications.
Furthermore, the society recommends that medical professionals conducting lip fillers treatments adhere to strict guidelines for patient selection, treatment planning, and post-procedure care. This includes ensuring that patients have realistic expectations about the outcome of the procedure and providing them with informed consent before proceeding with treatment.
Additionally, the EUCAPSM emphasizes the need for ongoing research and development in the field of lip fillers to improve their safety, efficacy, and longevity. The society encourages medical professionals and manufacturers to collaborate on studies that investigate new ingredients, technologies, and treatment approaches to advance the art of aesthetic plastic surgery.
The establishment of these safety protocols by the EUCAPSM is essential for promoting public trust in the lip filler industry and ensuring that patients receive high-quality treatments with minimal risk of complications. By prioritizing patient safety and well-being, the society aims to foster a more responsible and innovative approach to cosmetic surgery.
Lip filler materials are subject to strict regulatory approval and safety guidelines to ensure their safe use in aesthetic procedures.
The European Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery has established comprehensive guidelines for lip fillers, outlining recommendations for pre and postoperative care, as well as guidelines for the use of fillers in different facial areas.
These guidelines emphasize the importance of thorough patient evaluation, careful selection of the filler material, and meticulous technique to minimize the risk of adverse reactions or complications.
The guidelines also highlight the need for ongoing education and training for healthcare professionals administering lip fillers, emphasizing the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest research and technological advancements in the field.
Regulatory approval for lip filler materials is typically granted by national regulatory agencies, such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA), after demonstrating safety and efficacy through rigorous clinical trials.
The FDA, for example, has approved several lip fillers for cosmetic use, including hyaluronic acid dermal fillers, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid.
These materials are carefully evaluated for their biocompatibility, stability, and potential for causing adverse reactions, such as allergic responses or inflammation.
The EMA has also established its own guidelines for the authorization of lip fillers in Europe, which include requirements for robust clinical trials, safety monitoring, and post-marketing surveillance.
Furthermore, many countries have their own regulatory frameworks governing the use of lip fillers, such as Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) or the UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
These guidelines often require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products through clinical trials, which involve careful monitoring of patient outcomes and adverse reactions.
The guidelines also emphasize the importance of informed consent, ensuring that patients understand the potential risks and benefits associated with lip filler procedures and are aware of any necessary precautions or contraindications.
Additionally, many professional organizations, such as the European Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ESAPS), have established their own codes of practice and standards for the safe use of lip fillers in aesthetic procedures.
These guidelines often include recommendations for preoperative evaluation, including medical history taking and physical examination, as well as postoperative care, including monitoring for signs of adverse reactions or complications.
The ESAPS has established specific guidelines for lip filler use in different facial areas, such as the lips, cheeks, and nasolabial folds, highlighting the importance of careful selection of the filler material and technique to achieve optimal results while minimizing risk.
Furthermore, many manufacturers provide detailed technical specifications and product information, including ingredient lists, labeling claims, and contraindications, which help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about the safe use of their products.
Ultimately, regulatory approval and safety guidelines for lip fillers serve as a crucial safeguard to protect patients’ health and well-being during aesthetic procedures.
By ensuring that lip filler materials are thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy, regulatory agencies can help minimize the risk of adverse reactions or complications, allowing healthcare professionals to provide safe and effective treatments for their patients.
Read more about Mocha Kid Magazine here. Read more about Press on Honey here. Read more about Alkhemist LA here. Read more about Melissa Neufeld here.
- Sculptra Surrey – Collagen Stimulation Therapy Near Bramley, Surrey - January 1, 2025
- What Is Lip Filler Made Of - December 18, 2024
- Will I Regret Getting Fillers? - December 13, 2024
